Instrument Overview#
The instrumentation of the HALO aircraft is based on contributions from various universities and research institutions. Each instrument is developed and operated by an individual group, which leads to a modern instrumentation suite and well trained operators, but also requires to contact a range of people when working with data from HALO’s instruments. The purpose of this chapter is to introduce you to the individual contact points.
During the EUREC⁴A field campaign, the HALO aircraft had been outfitted in an updated “Cloud Observatory” configuration, much like as described by (Stevens et al., 2019). As the aircraft is build to be flying at high altitudes, most of the instrumentation observes the atmosphere (and in particular clouds) from the nadir perspective.
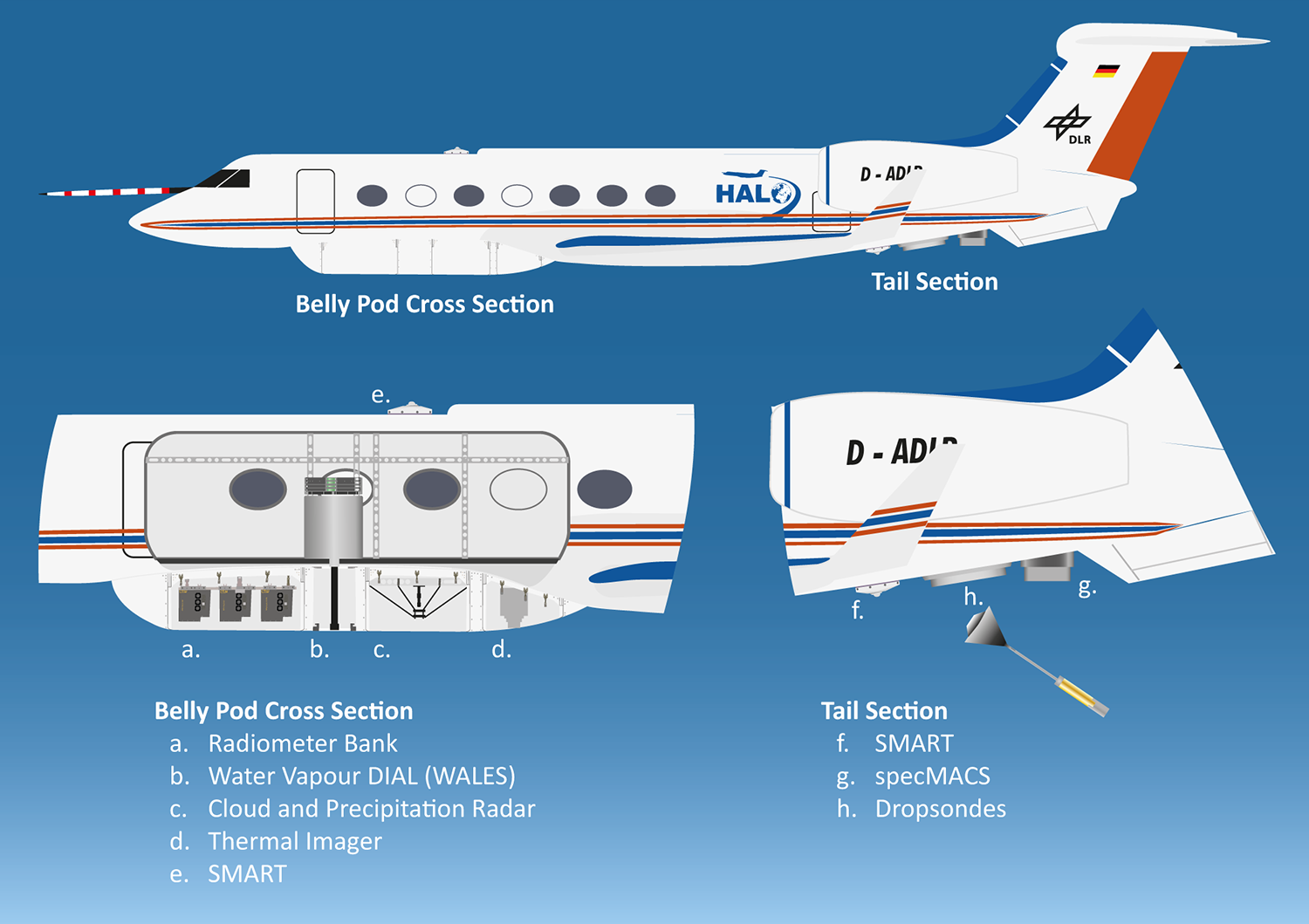
Fig. 1 Instruments on HALO as configured for the EUREC⁴A campaign.#
In particular, the instrumentation consists of broadband radiometers (BACARDI), basic instrumentation (BAHAMAS), a dropsonde launching system (Dropsondes), the active (radar) and passive microwave package (HAMP), irradiance spectrometers (SMART), a thermal imager (VELOX), an infrared radiometer (VELOX-KT19), a water vapor differential absorption lidar (WALES) and spectral and polarization resolving imagers (specMACS). You can find more detailed references to the instruments in the tabs below, as well as examples for data access in the upcoming chapters.
A set of broadband radiometer measuring upward and downward irradiance in the solar (0.2 - 3.6 micrometer) and terrestrial (4.5 - 42 micrometer) spectral range.
- home
- pi
- data provider
- home
- pi
- data provider
HAMP consists of a suite of passive microwave radiometers with 26 frequencies ranging between 22.24 and 183.31 GHz, and an active cloud radar measuring at 35.5 GHz. The radiometeres are installed nadir-pointing in a bellypod under the fuselage with opening angles between 2.7 (G-band) and 5.0° (K-band). The almost nadir-pointed radar antenna is located in a bellypod and connected to the electronics in the cabin. Pre-flight calibration was performed before each flight for the radiometers, and before the transfer flight to Barbados for the radar.
The Spectral Modular Airborne Radiation measurement sysTem (SMART) measures downward irradiances in the solar spectral range between 300 nm and 2200 nm.
- home
- pi
- data provider
- references
An Airborne Spectral Albedometer with Active Horizontal Stabilization
VELOX is a thermal infrared spectral imager (VELOX327k veL, 640 pixel by 512 pixels) with a synchronized filter wheel (at 100 Hz) covering six spectral channels in the thermal infrared wavelength range from 7.7 to 12.0 micrometer. The instrument measures the brightness temperature of upward radiance in a field-of-view of 35.49° by 28.71°.
- home
- pi
- data provider
Thermal infrared radiometer measuring the brightness temperature of nadir radiance between 9.6 and 11.5 micrometer. The field-of-view of 2.3° is located in the center of the VELOX images.
- home
- pi
- data provider
specMACS is the hyperspectral imager of the LMU in Munich. It measures from 400nm to 2500nm at a FOV of approximately 32° in a nadir looking perspective
